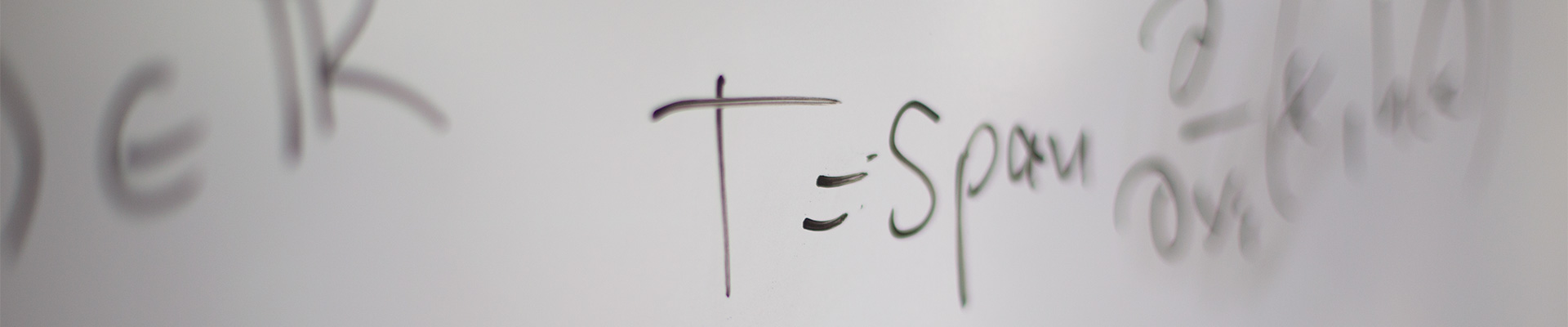Modulation instability in filamentary self-compression
Authors
- Brée, Carsten
- Demircan, Ayhan
- Steinmeyer, Günter
2010 Mathematics Subject Classification
- 78A60
2008 Physics and Astronomy Classification Scheme
- 42.65.-k 42.65.Jx 42.65.Re 42.65.Sf
Keywords
- Nonlinear Optics, Modulation Instability, Femtosecond Filamentation, Pulse compression
DOI
Abstract
We numerically analyze filamentary propagation for various medium- and input pulse parameters and show that temporal self-compression can greatly benefit from refocusing events. Analyzing the dynamical behavior in the second focal spot, it turns out that a dispersive temporal break-up may appear due to the emission of a hyperbolic shock-wave from the self-steepened trailing edge of the pulse. This break-up event enhances the self-compression capabilities of laser filaments, enabling up to 12-fold temporal compression. Only slightly perturbing the input pulse parameters, we further identify a regime in which refocusing events give rise to extended subdiffractive propagation in a weakly ionized channel.
Appeared in
- Laser Physics, 21 (2011) pp. 1313-1318.
Download Documents