xxxxxxxxxxbegin ENV["LANG"]="C" using Pkg Pkg.activate(mktempdir()) using Revise Pkg.add("Revise") Pkg.add(["PyPlot","PlutoUI","ExtendableGrids","GridVisualize", "VoronoiFVM"]) using PlutoUI,PyPlot,ExtendableGrids,VoronoiFVM,GridVisualize PyPlot.svg(true)end;Finite volumes: transient problems
Construction of control volumes
Start with a triangulation of a polygonal domain (intervals in 1D,triangles in 2D, tetrahedra in 3D).
Join triangle circumcenters by lines
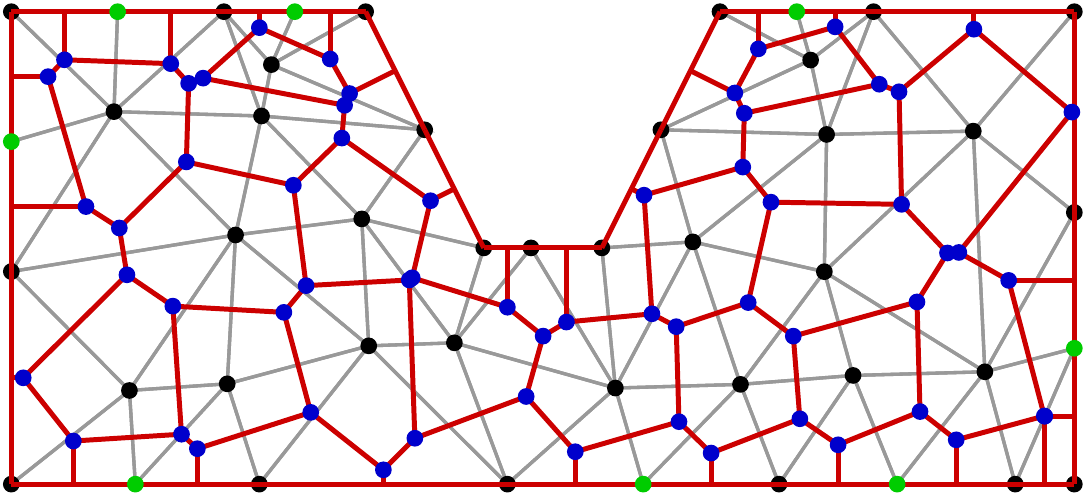
Black + green: triangle nodes
Gray: triangle edges
Blue: triangle circumcenters
Red: Boundaries of Voronoi cells
Condition on triangulation
There is a 1:1 incidence between triangulation nodes and Voronoi cells. Moreover, the angle between the interface between two Voronoi cells and the edge between their corresponding nodes is
Requires (in 2D) that sums of angles opposite to triangle edges are less than
"boundary conforming Delaunay property". It has different equivalent definitions and analogues in 3D.
Construction:
"by hand" (or script) from tensor product meshes
Mesh generators: Triangle, TetGen
Julia packages: Triangulate.jl, TetGen.jl; SimplexGridFactory.jl
The discretization approach
Use Voronoi cells as REVs aka control volumes aka finite volume cells.
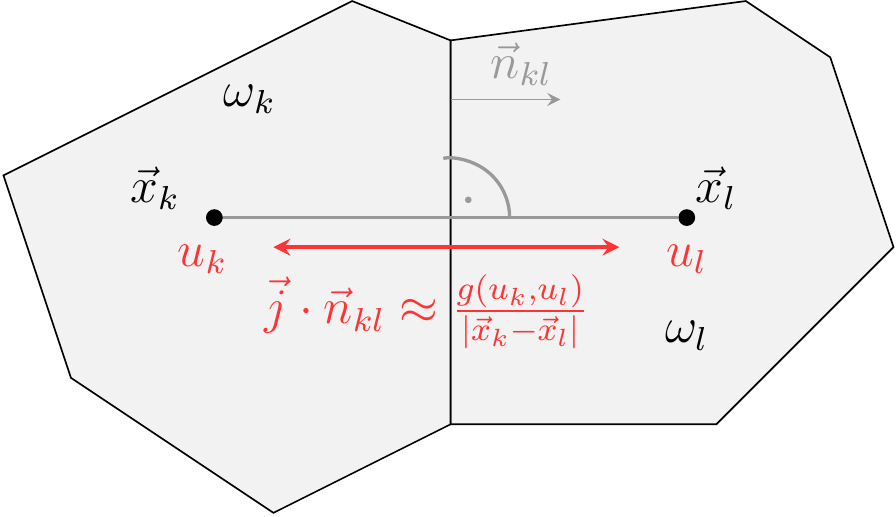
Given a continuity equation
Here,
Flux functions
For instance, for the diffusion flux
For a convective diffusion flux
where
Software API and implementation
The entities describing the discrete system can be subdivided into two categories:
geometrical data:
physical data: the number
This structure allows to describe the problem to be solved by data derived from the discretization grid and by the functions describing the physics, giving rise to a software API.
The solution of the nonlinear systems of equations can be performed by Newton's method combined with various direct and iterative linear solvers.
The generic programming capabilities of Julia allow for an implementation of the method which results in an API which consists in the implementation of functions
Examples
General settings
Initial value problem with homgeneous Neumann boundary conditions
evolution (generic function with 1 method)xxxxxxxxxx# Function describing evolution of system with initial value inival # using the Implicit Euler methodfunction evolution(inival, # initial value sys, # finite volume system grid, # simplex grid tstep, # initial time step tend, # end time dtgrowth # time step growth factor ) time=0.0 # record time and solution times=[time] solutions=[copy(inival)] solution=copy(inival) while time<tend time=time+tstep solve!(solution,inival,sys,tstep=tstep) # solve implicit Euler time step inival.=solution # copy solution to inivalue push!(times,time) push!(solutions,copy(solution)) tstep*=dtgrowth # increase timestep by factor when approaching stationary state end # return result and grid (times=times,solutions=solutions,grid=grid)endfpeak (generic function with 2 methods)xxxxxxxxxx# Define function for initial value $u_0$ with two methods - for 1D and 2D problemsbegin fpeak(x)=exp(-100*(x-0.25)^2) fpeak(x,y)=exp(-100*((x-0.25)^2+(y-0.25)^2))endcreate_grid (generic function with 1 method)xxxxxxxxxx# Create discretization grid in 1D or 2D with approximately n nodesfunction create_grid(n,dim) nx=n if dim==2 nx=ceil(sqrt(n)) end X=collect(0:1.0/nx:1) if dim==1 grid=simplexgrid(X) else grid=simplexgrid(X,X) endendDiffusion problem
diffusion (generic function with 1 method)xxxxxxxxxxfunction diffusion(;n=100,dim=1,tstep=1.0e-4,tend=1, D=1.0, dtgrowth=1.1) grid=create_grid(n,dim) ## Diffusion flux between neigboring control volumes function flux!(f,u,edge) uk=viewK(edge,u) ul=viewL(edge,u) f[1]=D*(uk[1]-ul[1]) end ## Storage term (under time derivative) function storage!(f,u,node) f[1]=u[1] end ## Create a physics structure physics=VoronoiFVM.Physics( flux=flux!, storage=storage!) sys=VoronoiFVM.DenseSystem(grid,physics) enable_species!(sys,1,[1]) ## Create a solution array inival=unknowns(sys) ## Broadcast the initial value inival[1,:].=map(fpeak,grid) evolution(inival,sys,grid,tstep,tend,dtgrowth)end xxxxxxxxxxresult_diffusion=diffusion(dim=1,n=1000);time=
Reaction-diffusion problem
Diffusion + physical process which "eats" species
reaction_diffusion (generic function with 1 method)xxxxxxxxxxfunction reaction_diffusion(; n=1000, dim=1, tstep=1.0e-4, tend=1, D=1.0, R=10.0, dtgrowth=1.1) grid=create_grid(n,dim) ## Diffusion flux between neigboring control volumes function flux!(f,u,edge) uk=viewK(edge,u) ul=viewL(edge,u) f[1]=D*(uk[1]-ul[1]) end ## Storage term (under time derivative) function storage!(f,u,node) f[1]=u[1] end ## Reaction term function reaction!(f,u,node) f[1]=R*u[1] end ## Create a physics structure physics=VoronoiFVM.Physics( flux=flux!, reaction=reaction!, storage=storage!) sys=VoronoiFVM.DenseSystem(grid,physics) enable_species!(sys,1,[1]) ## Create a solution array inival=unknowns(sys) ## Broadcast the initial value inival[1,:].=map(fpeak,grid) evolution(inival,sys,grid,tstep,tend,dtgrowth) endxxxxxxxxxxresult_reaction_diffusion=reaction_diffusion(dim=1,n=1000,R=10);time=
Convection-Diffusion problem
convection_diffusion (generic function with 1 method)xxxxxxxxxxfunction convection_diffusion(; n=20, dim=1, tstep=1.0e-4, tend=1, D=0.01, vx=10.0, vy=10.0, dtgrowth=1.1, scheme="expfit") grid=create_grid(n,dim) # copy vx, vy into vector if dim==1 V=[vx] else V=[vx,vy] end # Bernoulli function B(x)=x/(exp(x)-1) function flux_expfit!(f,u,edge) uk=viewK(edge,u) ul=viewL(edge,u) vh=project(edge,V) # Calculate projection v * (x_L-x_K) f[1]=D*(B(-vh/D)*uk[1]- B(vh/D)*ul[1]) end function flux_centered!(f,u,edge) uk=viewK(edge,u) ul=viewL(edge,u) vh=project(edge,V) f[1]=D*(uk[1]-ul[1])+ vh*0.5*(uk[1]+ul[1]) end function flux_upwind!(f,u,edge) uk=viewK(edge,u) ul=viewL(edge,u) vh=project(edge,V) f[1]=D*(uk[1]-ul[1])+ ( vh>0.0 ? vh*uk[1] : vh*ul[1] ) end flux! =flux_upwind! if scheme=="expfit" flux! =flux_expfit! elseif scheme=="centered" flux! =flux_centered! end ## Storage term (under time derivative) function storage!(f,u,node) f[1]=u[1] end ## Create a physics structure physics=VoronoiFVM.Physics( flux=flux!, storage=storage!) sys=VoronoiFVM.DenseSystem(grid,physics) enable_species!(sys,1,[1]) ## Assume homogeneous Neumann boundary conditions, so do nothig ## Create a solution array inival=unknowns(sys) ## Broadcast the initial value inival[1,:].=map(fpeak,grid) evolution(inival,sys,grid,tstep,tend,dtgrowth) end scheme:
xxxxxxxxxxresult_convection_diffusion=convection_diffusion(n=100, dim=1, scheme=scheme[1], vx=10,vy=10);time=
Brusselator system
Two species interacting via a reaction:
brusselator (generic function with 1 method)xxxxxxxxxxfunction brusselator(;n=100,dim=1,A=4.0,B=6.0,D1=0.01,D2=0.1,perturbation=0.1, tstep=0.05, tend=150,dtgrowth=1.05) grid=create_grid(n,dim) function storage!(f,u,node) f.=u end function bruss_diffusion!(f,_u,edge) u=unknowns(edge,_u) f[1]=D1*(u[1,1]-u[1,2]) f[2]=D2*(u[2,1]-u[2,2])end# Reaction:function bruss_reaction!(f,u,node) f[1]= (B+1.0)*u[1]-A-u[1]^2*u[2] f[2]= u[1]^2*u[2]-B*u[1]end# Create systembruss_physics=VoronoiFVM.Physics(flux=bruss_diffusion!,storage=storage!, num_species=2,reaction=bruss_reaction!)brusselator_system=VoronoiFVM.DenseSystem(grid,bruss_physics)enable_species!(brusselator_system,1,[1])enable_species!(brusselator_system,2,[1]) inival=unknowns(brusselator_system)for i=1:num_nodes(grid) inival[1,i]=1.0+perturbation*randn() inival[2,i]=1.0+perturbation*randn()end evolution(inival,brusselator_system,grid,tstep,tend,dtgrowth) endxxxxxxxxxxresult_brusselator=brusselator(n=500,dim=1);time=
Status `/tmp/jl_op3lMf/Project.toml` [cfc395e8] ExtendableGrids v0.7.4 [5eed8a63] GridVisualize v0.1.3 [7f904dfe] PlutoUI v0.7.2 [d330b81b] PyPlot v2.9.0 [295af30f] Revise v3.1.12 [82b139dc] VoronoiFVM v0.10.5